International Continence Society 2023, Toronto, Kanada, 27 - 29 Eylül 2023, ss.10, (Özet Bildiri)
Studies on the effects of various urinary biomarkers in children with neurogenic or non-neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) have been published in recent years. Three of them are Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP), Matrix Metallopreteinase-2 (MMP-2), and various positive effects in diagnosis and follow-up have been reported in different patient groups. In this study, it was aimed to evaluate the relationship of these urinary biomarkers with urodynamic findings and upper urinary tract deterioration (UTTD) in children with myelodysplasia.
Children with myelodysplasia evaluated in the pediatric urology outpatient clinic between 2022 and 2023 were included in the study. All patients underwent urinary ultrasonography, voiding cystourethrography, urodynamic studies, and DMSA renal scintigraphy. Children with missing data were excluded from the study. Urine samples were collected into sterile urine collection tubes before urodynamics. After each urine sample was centrifuged at 3000 g for 10 minutes, the supernatant was separated and stored at -800C until further analysis. In addition, control urine was collected from 10 healthy children. Urinary BDNF, ATP, and MMP-2 were studied by ELISA method. Urinary biomarker values of patients and controls were compared and subgroup analysis was performed in the myelodysplasia group in terms of urodynamic findings and UUTD. The presence of renal scar, vesicoureteral reflux, or hydronephrosis was considered as UUTD. Constipation status was evaluated with the Bristol stool chart.
The median age of 40 children (26 girls (65%), 14 boys (35%)) included in the study was 108 (8-216) months, and the healthy control group (6 girls, 4 boys) was 120 (60-154) months (p=0.981). The primary etiology of 35 children was myelomeningocele (87.5%), 2 dermal sinus (5%), 2 tethered cord (5%), and one sacrococcygeal immature teratoma (2.5%). Urinary BDNF, MMP-2, and ATP were found to be significantly higher in children with myelodysplasia compared to the control group (p=0.007, p=0.027, p=0.014, respectively) (Table 1). In the subgroup analysis, the three biomarker values were similar in children with bladder compliance below or above 10 cmH2O/ml (p=0.750, p=0.844, p=0.575). In addition, no difference was found in terms of UUTD in all three biomarkers (p=0.387, p=0.892, p=0.705). However, a negative correlation was found between urinary ATP and bladder compliance in the correlation analysis (p<0.05) (Table 2). Interestingly, a positive correlation was detected among the three biomarkers (p<0.01) (Table 2). There was no significant difference in urinary biomarkers between children with and without constipation.
Invasive urodynamic studies are the gold standard method in the evaluation of children with neurogenic LUTD after first-step tests. In recent years, it is tried to define tests that help and support urodynamic studies in the diagnosis and follow-up of these children. Among these, urine biomarkers come to the forefront with their easy-to-measure features. Three biomarkers evaluated in this study were found to be higher in children with myelodysplasia compared to the healthy control group. However, in subgroup analyses, they were not found to be significantly different in children with UUTD. One of these, urinary BDNF, is the most frequently studied biomarker in children with LUTD after NGF. Urinary BDNF has only been studied in one study in children with myelodysplasia, and decreased after the intravesical injection of botulinum toxin (1). Urinary MMP-2 has been previously studied in adults with spina bifida, and ATP in women with overactive bladders, and significant findings on both biomarkers have been reported (2,3). To our knowledge, these two biomarkers have been studied for the first time in children. In particular, we think that the negative relationship between urinary ATP and bladder compliance may be significant in clinical follow-up. The small number of patients seems to be the most important limitation of the study.
Urinary biomarkers seem promising for the future with their non-invasive features in the follow-up of children with neurogenic LUTD. However, the lack of standardization, the inconsistency between the results of the studies, and the inability to reliably predict risky groups are important shortcomings of urinary biomarkers. We consider that urinary biomarkers should only be assessed as a part of well-designed studies and should not be used in the clinical decision-making process of neurogenic LUTD in children.
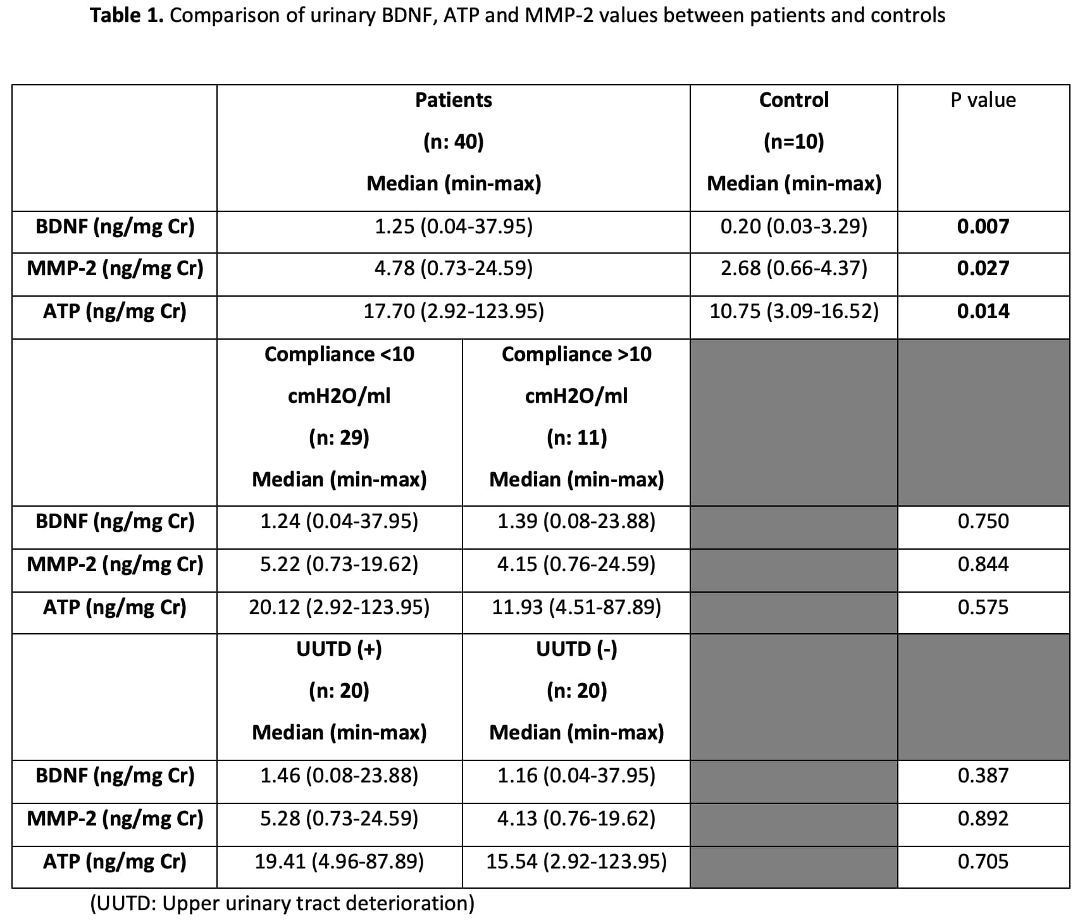 Table 1. Comparison of urinary BDNF, ATP and MMP-2 values between patients and controls
Table 1. Comparison of urinary BDNF, ATP and MMP-2 values between patients and controls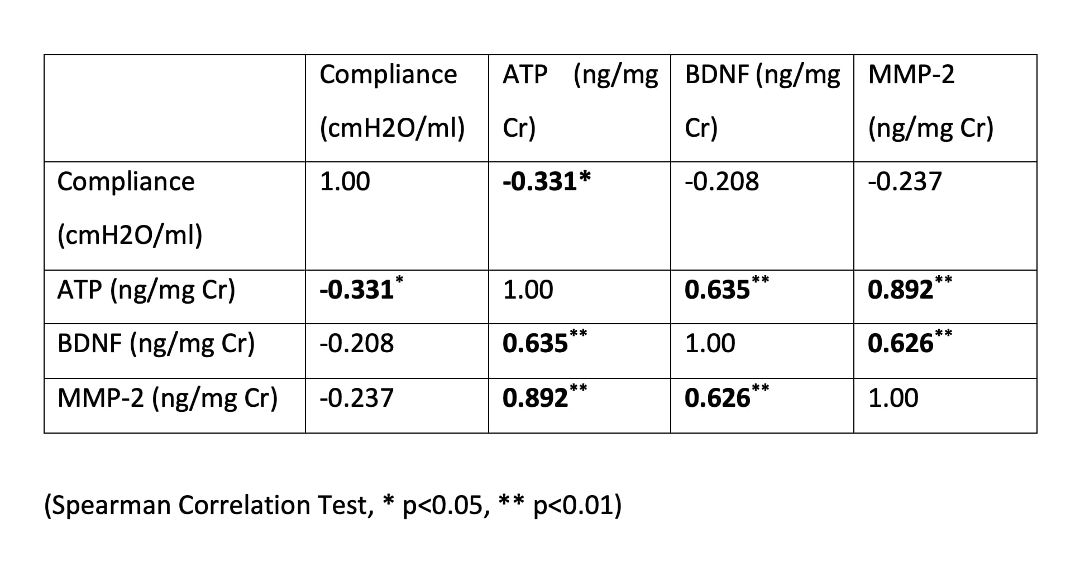 Table 2. Correlations for bladder compliance, ATP, BDNF and MMP-2 in patients
Table 2. Correlations for bladder compliance, ATP, BDNF and MMP-2 in patients
- Sekerci CA, Tanidir Y, Toprak T, Basok BI, Isman F, Simsek F, et al. Value of Urinary Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels on the Assessment of Botulinum Toxin Type A Treatment for Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity in Children with Myelodysplasia. J Urol. 2019;201(1):174-80.
- Peyronnet B, Richard C, Bendavid C, Naudet F, Hascoet J, Brochard C, Senal N, Jezequel M, Alimi Q, Khene ZE, Corlu A, Clément B, Siproudhis L, Bouguen G, Kerdraon J, Manunta A, Gamé X. Urinary TIMP-2 and MMP-2 are significantly associated with poor bladder compliance in adult patients with spina bifida. Neurourol Urodyn. 2019 Nov;38(8):2151-2158. doi: 10.1002/nau.24163. Epub 2019 Sep 4. PMID: 31486131.
- Silva-Ramos M, Silva I, Oliveira O, Ferreira S, Reis MJ, Oliveira JC, Correia-de-Sá P. Urinary ATP may be a dynamic biomarker of detrusor overactivity in women with overactive bladder syndrome. PLoS One. 2013 May 31;8(5):e64696. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064696. PMID: 23741373; PMCID: PMC3669404.